An ectopic pregnancy is a condition that occurs when a fertilized egg implants somewhere other than the uterus. Over 90% of ectopic pregnancies occur in the fallopian tubes (the tube-like organ that connects the ovaries to the uterus). As the pregnancy grows, a rupture of the fallopian tube can cause life-threatening internal bleeding, which may require emergency surgery.
WHAT ARE THE RISK FACTORS FOR AN ECTOPIC PREGNANCY?
About half of all women who have an ectopic pregnancy have no known risk factors. However, the following factors can increase the risk:
- Having a history of a previous ectopic pregnancy.
- Having had previous surgery on the fallopian tubes.
- A history of pelvic or abdominal surgery.
- Certain sexually transmitted infections.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
- Endometriosis.
- Smoking.
- Getting pregnant while using an intrauterine device (IUD).
- Being over the age of 35.
- Using assisted reproductive technologies, such as IVF treatment, also increases the risk of an ectopic pregnancy.
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF AN ECTOPIC PREGNANCY?
In the beginning, an ectopic pregnancy shows similar symptoms to a normal pregnancy, such as a missed period, breast tenderness, nausea, and a positive pregnancy test. It can be difficult to know if you are having an ectopic pregnancy or a healthy one if you have abnormal vaginal bleeding, lower back pain, mild pain in the abdomen or pelvis, or mild cramping on one side of the pelvis. In cases of abnormal bleeding, pain in the lower abdomen, and a positive pregnancy test, you should see a gynecologist immediately to check for the possibility of an ectopic pregnancy.
As an ectopic pregnancy grows, and especially if a fallopian tube ruptures, more serious symptoms can develop, such as sudden, severe pain throughout the abdomen or in the lower abdomen, dizziness, and fainting. This could be a sign of life-threatening internal bleeding. You should go to the emergency room as soon as possible.
HOW IS AN ECTOPIC PREGNANCY DIAGNOSED?
When an ectopic pregnancy is suspected, a blood test is done to measure the level of the pregnancy hormone (beta-hCG) along with an abdominal examination. In addition, an ultrasound is performed to see if the gestational sac is inside or outside the uterus. While a diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy can sometimes be made immediately with the examination and test results, these tests may often need to be repeated every few days.
HOW IS AN ECTOPIC PREGNANCY TREATED?
An ectopic pregnancy can be treated in two ways: with medication or with surgery.
WHAT MEDICATIONS ARE USED TO TREAT AN ECTOPIC PREGNANCY?
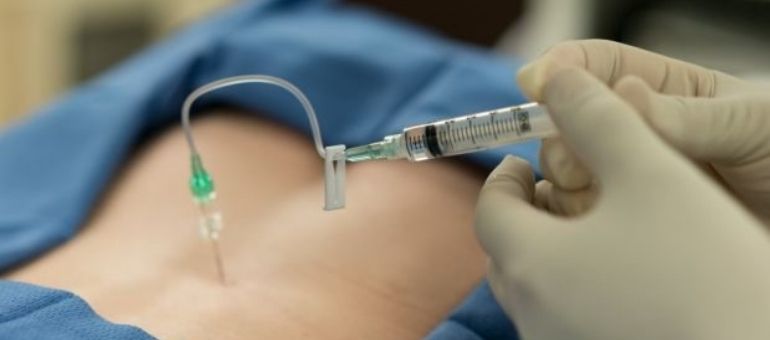
The most common medication used to treat an ectopic pregnancy is methotrexate. This drug stops the growth of the cells and the embryo, which ends the pregnancy. With this treatment, there is no need to remove the fallopian tube.
Your doctor will decide to use methotrexate based on various factors, such as the level of pregnancy hormones, the size of the gestational sac, the presence of an embryonic heartbeat, and whether the fallopian tube has ruptured. One of the most important factors is whether you can have regular blood tests after the medication treatment. You cannot use methotrexate if you are breastfeeding or have a significant health problem like liver disease.
Methotrexate is often given as a single injection in the hip. Before you receive methotrexate, blood tests should be done to measure hCG levels and the function of certain organs. If your hCG levels do not drop enough after the first dose, an additional dose of methotrexate may be given.
WHEN IS SURGERY USED TO TREAT AN ECTOPIC PREGNANCY?
If an ectopic pregnancy is diagnosed late and its termination is delayed, the fallopian tubes may be stretched, torn, or ruptured. In these cases, emergency surgery is necessary. Sometimes, even if the fallopian tube has not ruptured, surgery may be necessary for patients who would not benefit from methotrexate treatment. In these situations, the ectopic pregnancy may be removed from the tube, or the entire tube may be removed along with the pregnancy. The surgery is typically done with laparoscopy, a procedure that uses a thin, lighted camera inserted through small incisions in the abdomen.
CAN AN ECTOPIC PREGNANCY BE PREVENTED?
Most of the time, an ectopic pregnancy cannot be prevented.
CAN AN ECTOPIC PREGNANCY AFFECT FUTURE PREGNANCIES?
When you have had an ectopic pregnancy, your risk of having another ectopic pregnancy increases. During future pregnancies, you should be vigilant for the signs and symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy until your doctor confirms that the gestational sac is growing in the correct location. You should have regular check-ups before and during pregnancy.